
Public vs Private Blockchain RPC Nodes: What’s Best?
When it comes to interacting with blockchain networks, RPC (Remote Procedure Call) nodes play a critical role. These nodes allow users and applications to read blockchain data, submit transactions, and interact with smart contracts — all without dealing with the complexities of network communication.
In this article, we’ll break down the differences between public and private blockchain RPC nodes and help you determine which is best for your use case, whether you’re building decentralized applications (dApps), managing blockchain interactions, or prioritizing performance and privacy.
What Are Blockchain RPC Nodes?
RPC nodes serve as gateways that enable users to connect with a blockchain. Through RPC interfaces, developers and users can retrieve data from the blockchain, send transactions, and execute smart contracts. However, the choice between public and private RPC nodes can significantly affect performance, security, and scalability.
Let’s dive into the differences and understand when to choose public or private blockchain RPC nodes.
Public Blockchain RPC Nodes: Fast, Free, and Shared
A public RPC node is an open-access endpoint that allows anyone to connect with a public blockchain like Ethereum, Bitcoin, or Cardano. Public RPC nodes are typically managed by third-party providers and are shared among users worldwide. Some popular providers include Infura, Alchemy, and QuickNode.
Public RPC nodes are usually used for the development of decentralized applications (dApps), wallet services, and because of its public nature, access to blockchain data to users all over the world. In terms of infrastructure, contrary to private nodes, public ones are managed by a third-party provider or blockchain developers and it’s shared between users and other developers and services. Public RPC nodes are provided by companies to blockchain networks. Ethereum, for example, uses Infura, Alchemy, and Quicknode, while Cardano uses Blockfrost.
Benefits of Public RPC Nodes:
Public RPC nodes are great for users and developers who want quick access to blockchain data for testing and building, as they won’t need to set up the node themselves. Because they’re managed by a third party, there’s no need for users to worry about maintenance or updates. The costs of using a public RPC are also lower, and sometimes even free.
Drawbacks of Public RPC Nodes:
As for security, since these nodes are accessible by anyone, IP addresses, and transaction behavior can be exposed, therefore potentially more susceptible to data leaks and surveillance — this also raises privacy concerns, as those data leaks can contain sensitive information from the users that can be used for malicious acts. Public RPC nodes aren’t customizable, so users have no say in configuration.
The shareable nature of public nodes might make them lag in terms of performance. They’re more prone to congestion, which in turn can lead to slower response times and rate-limiting issues during network peaks.
Also, there’s a rate limit, which doesn’t happen with private RPC nodes. Since public ones are shared amongst numerous users, there are usually restrictions on the number of requests — these can be set per minute or day.
Confidential Public Blockchain RPC Nodes: Enhanced Privacy with Convenience
Confidential public RPC nodes offer a unique balance between the openness of traditional public nodes and the control of private ones. While still accessible to the general public, they incorporate advanced privacy-enhancing technologies such as IP masking, encrypted connections, and confidential transaction protocols to ensure greater data protection. This allows users to interact with blockchain networks without exposing sensitive information like their IP address or transaction details to third parties.
These nodes cater to users who need the convenience and accessibility of public nodes but are unwilling to compromise on privacy. Developers working on privacy-focused decentralized applications (dApps) find confidential public nodes particularly useful, as do individuals seeking anonymous interaction with blockchain networks. They are also an attractive option for anyone concerned about data tracking or surveillance when using public nodes.
Benefits of Confidential Public RPC Nodes:
The key benefit of confidential public RPC nodes is their enhanced privacy. By employing encryption and other privacy techniques, these nodes significantly reduce the risk of exposing sensitive user data. Like standard public nodes, they require no complex infrastructure setup since they are managed by external providers, making them easy to use. Additionally, some confidential nodes offer improved security through integrated measures like encrypted communication or privacy protocols such as zk-SNARKs, further protecting user data.
Drawbacks of Confidential Public RPC Nodes:
However, there are some drawbacks. Users have limited control over the node’s configuration, as with regular public nodes. Depending on the privacy features implemented, there may also be slight performance trade-offs. Confidential public nodes are still a relatively new technology, meaning they are not as widely available as traditional public nodes, which may limit options for users.
Some notable examples of confidential public RPC nodes include Mystiko.Network, which offers decentralized, private RPC access using privacy-enhancing techniques, and Blockdaemon Confidential RPCs, which provide secure and confidential endpoints for public blockchain interaction.
Private Blockchain RPC Nodes
Private RPC nodes are not accessible to the public. The node is owned and operated by a specific individual, company, or organization, and access is restricted to authorized users. Setting them up requires technical expertise in configuring, maintaining, and solving issues that might arise.
They are ideal for enterprises that need high levels of performance, but also privacy and control over their blockchain interactions. It’s also a good solution for developers looking to avoid rate limits and who want to configure the node themselves. Other people who might prefer using private RPC nodes include users who prioritize security because they are in control of their own data.
Benefits of Private RPC Nodes:
Privacy is a key feature and is why some people prefer private nodes to public ones — the operator has full control over the data, which means there are no third parties involved in the process. Performance is usually higher since there are no rate limits for the issuing amount.
Drawbacks of Private RPC Nodes:
The fact that these nodes are privately managed and maintained requires deeper technical knowledge of how to set them up, their own architecture, and also more resources — such as hardware, storage, network bandwidth). Setting up a private RPC node is a complex task, which is why is recommended for developers and people who are familiar with these.
While most interactions with these blockchains happen through public nodes, organizations can run private instances of these blockchain nodes for more control and security.
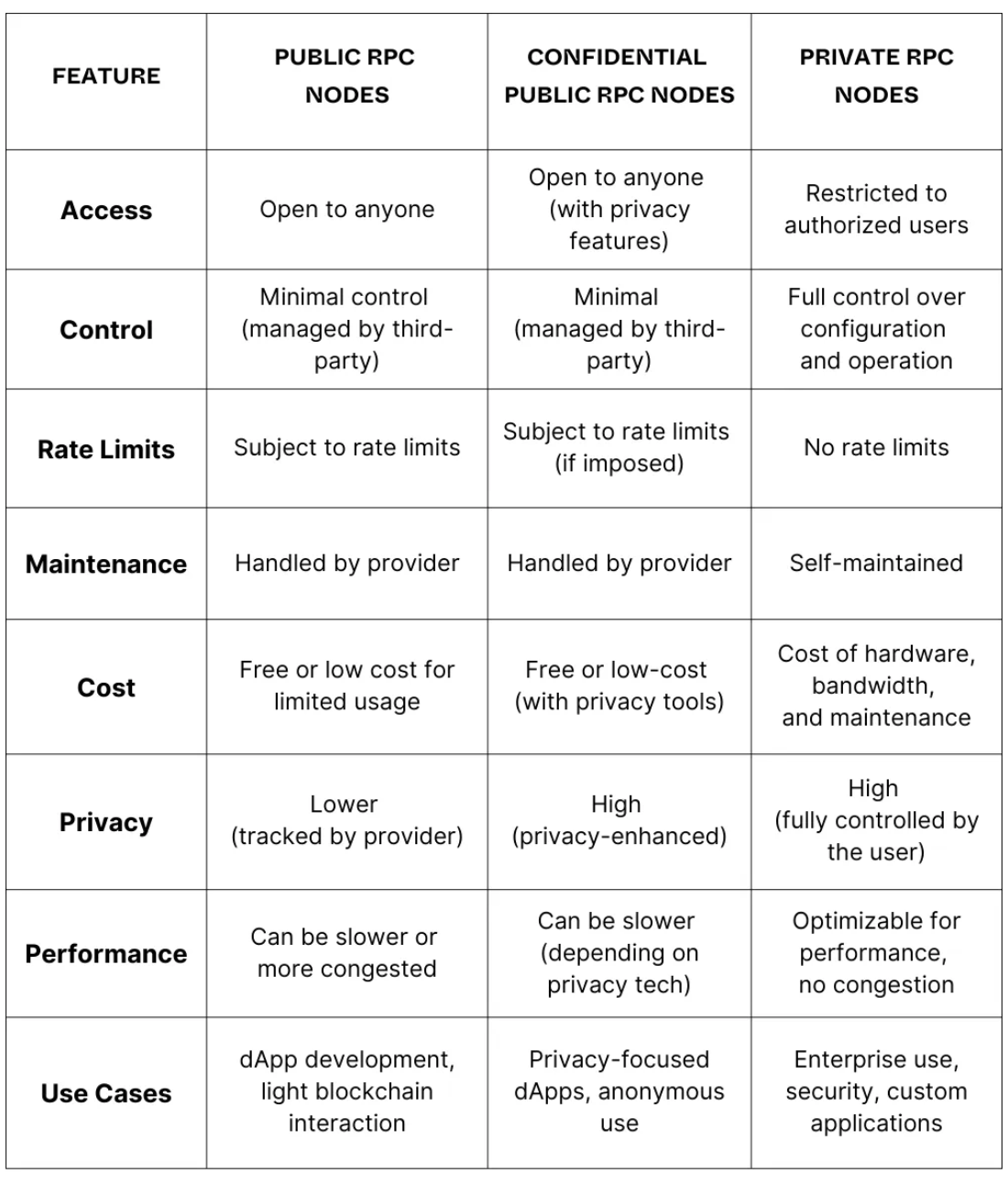
When to Choose Public vs. Private RPC Nodes
Choose Public RPC Nodes if:
- You’re developing or testing a dApp and need easy access to blockchain data.
- You need quick, cost-effective access without dealing with infrastructure maintenance.
- Performance and privacy aren’t your top concerns.
Choose Confidential Public RPC Nodes if:
- You want the convenience of public RPC access but with additional privacy features.
- You’re building or using privacy-focused applications and want to minimize data exposure.
- You need blockchain access but have concerns about IP tracking and transaction metadata visibility.
Choose Private RPC Nodes if:
- Your business requires complete control over the node’s configuration, security, and performance.
- You’re running an enterprise application that demands high security and optimized performance.
- You want to avoid rate limits and have the resources to manage and maintain your own infrastructure.
Conclusion: Public, Confidential Public, or Private RPC Nodes — Which Is Best for You?
The choice between public, confidential public, and private RPC nodes depends on your specific blockchain needs. Public RPC nodes are ideal for low-cost, easy access, while confidential public RPC nodes offer enhanced privacy without sacrificing convenience. For maximum control, privacy, and performance, private RPC nodes are the way to go, though they come with greater complexity and costs.
By weighing the trade-offs between accessibility, privacy, and performance, you can make the right decision for your project.
• • •
About Integritee
Integritee is the most scalable, privacy-enabling network with a Parachain on Kusama and Polkadot. Our SDK solution combines the security and trust of Polkadot, the scalability of second-layer Sidechains, and the confidentiality of Trusted Execution Environments (TEE), special-purpose hardware based on Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX) technology inside which computations run securely, confidentially, and verifiably.
Community & Social Media: Join Integritee on Discord | Telegram | Twitter | Medium | Youtube | LinkedIn | Website
Products: L2 Sidechains | Trusted Off-chain Workers | Teeracle | Attesteer | Securitee | Incognitee
Integritee Network: Governance | Explorer | Mainnet | Github
You Might Also Like
An Infinity of Use Cases for NFTs: From Real Estate to Supply Chain
Blockchain and Cybersecurity: Can Decentralization Solve the Biggest Security Challenges?
AI & Confidential Computing: Building Trustworthy AI Applications with TEEs
Common European Data Spaces: Fostering Data Innovation & Collaboration in the EU
How Biometric Data Collection Can Be Dangerous — Even When Built With Blockchain
Hyperautomation: The Power of Blending AI, Blockchain, and RPA
Cybercrime on the Rise: Why Is Securing OT Systems Paramount?
For the Greater Good: Using Blockchain for Social Change
Bug Bounty Programs: How Outsourcing Can Help Your Project
DePINs: Harnessing the Power of Connectivity to Build Real-World Applications
MiCA & Other Crypto-Related Regulations: Striking the Right Balance
DEXs on Polkadot: Leveraging the Power of Substrate & Shared Security
Slot Auctions vs Coretime: What’s Changing for Polkadot Projects
DEXs: The What, The Why & The How of Decentralized Exchanges
The Potential of Tokenizing Assets: From Houses to Private Equity & Whisky
Embracing Unpredictability: The Role of Randomness in Blockchain
Uncovering Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms: Proof-of-Stake, Proof-of-Work & Beyond
Decoding CBDCs: Advantages & Challenges in the Digital Monetary Landscape
Unleashing Scalability and Speed: The Importance of Layer 2 Blockchain Solutions
Bear With Us: Blockchain Technology is Still Relevant, Even when Crypto Declines
The Imperative for Privacy in Blockchain: TEEs & Privacy-Preserving Software
How Blockchain is Benefiting Numerous Industries: From Sustainability to Brand Quality Control
KYC in Web3: How DiD is Saving the Day for Projects & Companies
Blockchain in Aerospace: Reducing Costs & Enhancing Efficiency
DAOs: How Fair can Decision-Making be and Why is Private Voting Essential?
Web3 Bounties: Rewarding Developers with Tokens
Digital Twins: Increasing Efficiency Without Compromising Privacy
